Following are free excerpts from section II.I.II of my recent book “Philosophy Unscrambles Dark Matter”.

II.I.II. The actual Anomalies
Not only that redshifts of far off galaxies are not due to Doppler’s Effect and thus do not represent radial velocities, there are also genuine problems in the established distances of those galaxies. Official distances of nearer objects have been determined by using common techniques of geometry and these distances are correct. The case of far off galaxies was challenging where finally a method to use luminosity of certain kind of stars (i.e. Cepheid Variable) as indicator of distance was adopted. Theory of redshift-distance relationship was already published where distances had been determined on the basis of luminosity alone and it was afterwards that important works of Fritz Zwicky (1933 and 1937) emerged where he analyzed a huge cluster of galaxies with respect to the total size as well as luminosity and redshift profiles of individual member galaxies of that cluster. The type of Zwicky’s analysis offered a great signal concerning the applicability of straightforward geometrical technique for the determination of galactic distances but unfortunately the hint was taken up by the Expansionists (i.e. relativists) and never brought to the general view in the original simpler form because after sensing the anomaly in this aspect, Expansionists distorted the facts and implemented the hint within twisted expansionist terminology and framework to keep the anomalous results hidden from view. Before discussing the hint, it is better to apply simple technique of geometry to determine the distances of (i) Moon and; (ii) the Sun.

Here we have taken standard values for ‘angle of view’ and ‘diameters’ of Moon and the Sun from online sources[i]. Our calculated distances of both the objects are only slightly different from official distances therefore we regard this method as accurate for the purpose of evaluating the distance. The hint that we get from the works of Zwicky is that he has estimated or determined the total diameter of the Coma Cluster. In his 1937 paper, he has taken radius of Coma Cluster to be only 2 million light years which is actually wrong as the up-to-date official estimate is 10 million light years and the reason of underestimation was that by that time, distance of Coma Cluster was also underestimated to be only 45 million light years which, by modern and ‘finalized’ standard is almost 321 million light years. The hint that now we can get is that the diameter is 20 million light years[ii] that should form an ample measurable angle of view on the sky. Now, instead of relying on measurements of the distances on the basis of luminosity, let us here calculate the distances of few prominent astronomical objects on the basis of simple geometry.
We have seen that the above method of distance estimation of astronomical objects requires (i) angle of view on sky and; (ii) actual or approximate diameter of the object. Historically, the estimates regarding distances of beyond Milky Way galaxies started in 1920s on the basis of luminosity of certain kind of stars because perhaps no data, calculation or approximation about diameters of those astronomical objects was available at that time. In 1930’s, works of Fritz Zwicky and others featured estimates regarding diameters of astronomical objects located far beyond Milky Way. Initially those estimates were wrong but they were improved and corrected over time. Angles of view on sky of those astronomical objects were also not difficult to figure out that were determined eventually but matters were in the hands of Expansionists who contaminated simple techniques of geometry with formulas of redshifts,[iii] possibly after having sensed the type of anomalies that must have surfaced in case the straightforward methods were implemented. As a matter of fact, so far simple distance determination method has not been applied[iv] even for the case of Andromeda which is the nearest large galaxy; whose official diameter in light years is known[v] and angle of view on sky is also known[vi] to be slightly larger than six times the angle of moon. Likewise the estimate regarding diameter of Coma Cluster is available and angle of view on sky is also known to be almost four times the angle of moon[vii]. Here, for our analysis, we select another astronomical ‘object’ i.e. the famous Hubble Deep Field image that belongs to tiny section of sky whose angle of view on sky is almost 10 times smaller[viii] than that of moon but contains ten times more galaxies than Coma Cluster due to which we can get a rough but safe (lower side) estimate of diameter of almost 60 million light years because with almost 1000+ galaxies, from edge to edge, there should be average 33 galaxies in Coma Cluster and with 10000 galaxies in deep field image, the number of edge to edge galaxies should be 100 which is three times greater therefore we take diameter of deep field image to be three times greater than that of Coma Cluster. We however regard it as lower side safe estimate because deep field is not a cluster of relatively compacted galaxies (having compressed in-between distances) which is the case with Coma Cluster.

By applying the straightforward geometrical method we get following ‘anomalous’ estimates of distances of these astronomical objects:

For Andromeda Galaxy, we notice a large discrepancy in the distance of 3.9 million light years calculated through straightforward geometry in comparison with the official distance which is only 2.5 million light years. Likewise, the official distance of Coma Cluster is only 321 million light years but geometry is telling it should be located at almost 509 million light years. And the case of Deep Field Image is particularly ‘anomalous’ because the calculated distance is located far beyond the permitted zone of the so-called standard model. Readers are requested to recalculate these figures by themselves to see the genuineness of the results. For instance, how come a huge cluster of galaxies that contains almost 1000 separate galaxies having large distances in-between as well, forms a smaller than a single galaxy Andromeda’s angular view on sky and yet located at distance of only 321 million light years when Andromeda, a single galaxy, itself is officially located at 2.5 million light years? A very large object that is larger by ratio of many thousands and not by ratio of only many hundreds is appearing smaller – it means that distance of the object must not be as low as only 321 million light years. It is making perfect sense that Coma Cluster’s actual distance is more than 500 million light years.
It is stated earlier that so far straightforward geometric method has not been applied for distance estimation even for the case of Andromeda which is the nearest large galaxy and whose diameter as well as angle of view on sky is known. Following section of Wikipedia article explains which methods have been applied so far and anyone should wonder why simple geometry has not been applied so far[ix]:
Distance estimate
At least four distinct techniques have been used to estimate distances from Earth to the Andromeda Galaxy. In 2003, using the infrared surface brightness fluctuations (I-SBF) and adjusting for the new period-luminosity value and a metallicity correction of −0.2 mag dex−1 in (O/H), an estimate of 2.57 ± 0.06 million light-years (1.625×1011 ± 3.8×109 astronomical units) was derived. A 2004 Cepheid variable method estimated the distance to be 2.51 ± 0.13 million light-years (770 ± 40 kpc).[2][3] In 2005, an eclipsing binary star was discovered in the Andromeda Galaxy. The binary[c] is two hot blue stars of types O and B. By studying the eclipses of the stars, astronomers were able to measure their sizes. Knowing the sizes and temperatures of the stars, they were able to measure their absolute magnitude. When the visual and absolute magnitudes are known, the distance to the star can be calculated. The stars lie at a distance of 2.52×106 ± 0.14×106 ly (1.594×1011 ± 8.9×109 AU) and the whole Andromeda Galaxy at about 2.5×106 ly (1.6×1011 AU).[4] This new value is in excellent agreement with the previous, independent Cepheid-based distance value. The TRGB method was also used in 2005 giving a distance of 2.56×106 ± 0.08×106 ly (1.619×1011 ± 5.1×109 AU).[5] Averaged together, these distance estimates give a value of 2.54×106 ± 0.11×106 ly (1.606×1011 ± 7.0×109 AU).[a] And, from this, the diameter of Andromeda at the widest point is estimated to be 220 ± 3 kly (67,450 ± 920 pc).[original research?] Applying trigonometry (angular diameter), this is equivalent to an apparent 4.96° angle in the sky.
From the above quoted text from the Wikipedia article, the very last sentence is particularly important. This sentence is not supported through citation and it seems that this sentence has been added by some curious individual who actually applied trigonometry on accepted diameter and distance of Andromeda galaxy and found that angle of view on sky should be 4.96°instead of official and observed value of 3.167°. Therefore we now put the value of 4.96° in our straightforward geometry for the case of Andromeda and note that with 4.96° angle of view on sky, the calculated distance of Andromeda galaxy tallies with the official distance of 2.54 million light years.
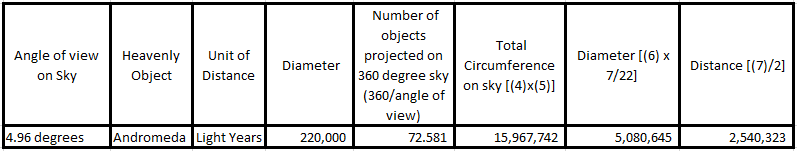
Here we see that someone’s independent calculations using official Trigonometry have confirmed the results of our commonsense based straightforward geometric formula. It is clear that if Andromeda is actually located at distance of just 2.54 million light years then it should form a larger angle of view of 4.96°which is larger than actually observed angle of view of only 3.167°. Therefore, the official distance of Andromeda galaxy is not supported by the known diameter and angle of view on sky as the official distance defies official Trigonometry.
The case of Deep Field Image is anomalous and complex as well because this image covers galaxies located at wider range of distances along line of sight. But if ‘nearer’ galaxies or objects are included in this image whose total angular diameter on sky is just one tenth that of moon then those ‘nearer’ galaxies also must be located very far away. For example up to the distance of Coma Cluster, only 20-30 galaxies should fill this image in complete. The angular diameter of deep field image is almost 45 times smaller than that of Coma Cluster yet contains 10 times more galaxies within a very small angle on sky. Roughly there should be only few hundred ‘foreground objects’ such that the ‘foreground’ also should be located very far away. The difficulty of ‘foreground objects’ however has been greatly solved through ‘Extreme Deep Field Image’ which is actually a close-up assessment of the core or nucleus of the same Deep Field Image where 5500 galaxies are assessed but angle of view is also reduced to become almost 14th the angular size of moon. The overall implication regarding distance estimation should remain almost same. Having total 10000 galaxies with margin of few hundred ‘foreground objects’, the diameter from edge to edge has been taken only at 60 million light years which is a safe lower side estimate because official estimate of diameter of Coma Cluster with only 1000 and squeezed galaxies is 20 million light years. Furthermore, if we remove the foreground objects from the deep field image then even greater number of background objects will be exposed and total number of galaxies in the image will be increased. It is safe lower side estimate also because if we consider another perspective that distance between small dot at one edge and another small dot on opposite edge should be at least the distance between Milky Way and one of the galaxies of Coma Cluster which is actually located at 500 million light years but still lies within our cosmic neighborhood then the estimate of distance of the farthest galaxy in the deep field image reaches to almost 583 billion light years from earth. The moderate estimate can be something like 20-40% of the higher side estimate thus those farther galaxies of deep field image, with moderate estimate, may be located at distance of 100 to 200 billion light years. We can attempt to get more precise result on our moderate estimate of distances. The Deep Field Image officially contains 10000 galaxies that include many foreground larger galaxies also. If we remove foreground galaxies then even more small looking galaxies are expected to be revealed from behind the foreground objects. But for the sake of our moderate estimate, we say there are only 10000 background small looking galaxies. From edge to edge, only 100 galaxies (each 80000 light years across) exist and galaxies are separated by the moderate distance of two million light years each. With these settings, we get edge to edge diameter of 208 million light years of the background visible extent of Hubble Deep Field Image. With this precise moderate estimate of diameter, the distance of those farthest visible (small looking) galaxies in Deep Field Image comes at 238.254 billion light years. Even at safer lower side estimate of 68 billion light years, this is serious discrepancy of the standard model where the viewable galaxies must not cross the distance of 13.2 billion light years only to remain conforming to the standard age of the universe of 13.8 billion years.
With huge distance scale of many hundred billion light years, the farthest galaxies ‘look’ small due to obvious reasons. But NASA loves to tell us that those galaxies are actually smaller in size and their ‘standard’ reason is also obvious because at distance of only 13+ billion light years, large galaxies should not have appeared so small. NASA very conveniently informs us that earlier galaxies are actually smaller in size in following words[x]:
When we look at very distant galaxies, we see a completely different picture. Many of these galaxies tend to be small and clumpy, often with a lot of star formation occurring in the massive knots.
In my opinion, the farthest visible galaxies, being located at distance scale of many hundred billion light years are typically very large galaxies as smaller ones simply could not be seen from such huge distances. NASA insists that they are smaller in size only to project them on a little and unrealistic but ‘standard’ distance scale of just 13+ billion light years. When a galaxy actually located at distance of many hundred billion light years is declared to be located at only 13+ billion light years then ‘yes’ it is smaller in size and may also be ‘half manufactured’ sort of. In case background small looking galaxies of Deep Field Image are located at 13.5 billion light years then edge to edge diameter of background visible extent of this image should be only 11.8 million light years which is almost equal to the diameter of our small local group[xi] that contains only three large galaxies along with just 50 other dwarf galaxies. Wikipedia article about current record holder of farthest galaxy[xii] informs us that diameter of this farthest galaxy ‘GN-z11’ is only 25000 light years. If diameter of visible background extent of Deep Field Image is only 11.8 million light years then from edge to edge there are 100 small galaxies each having diameter of only 25000 light years and each separated by distance of only 93000 light years and result would be what NASA wants to tell that those background smaller galaxies are located at distance of only 13+ billion light years. These results do not match with the actual Deep Field Image whose careful glimpse reveals very sparse density of galaxies such that edge to edge smaller looking galaxies are seemingly separated by more than our previous moderate estimate of 2 million light years each. In fact the claim of standard model cosmology that early universe was ‘denser’ is not actually confirmed as farthest galaxies in Deep Field Image are not denser than our local density of galaxies. For this reason official people often say that early ‘dense’ universe can be seen in CMB only because ‘early’ galaxies do not show the desired high density. The actual background small looking galaxies are in fact very large galaxies and from edge to edge they are separated by very large distances – far more than our previous moderate figure of 2 million light years. By no means can they fit within diameter of only 11.8 million light years and thus by no means they can reasonably demonstrated to be located at distance of only 13+ billion light years.
The primary objective of this book is not to highlight the discrepancies of the Big Bang Cosmology. Basically two reasons persuaded me to include these anomalies in this section of the book – firstly the readers should forget the so-called ‘anomaly’ of dark matter and should think about the actual anomalies. Secondly, it seemed appropriate to repeat the pattern of Fritz Zwicky in presenting apparently out of context anomaly within the discussion of a separate topic. As far as clusters of galaxies are concerned, there is no genuine anomaly of ‘dark matter’ because redshifts do not mean ‘radial velocities’ and actually there is no ‘velocity dispersion’ within the cluster; Zwicky was also trying to assert the same thing. The actual anomaly whose hint comes from study of cluster as a whole is the anomaly in the official distances of astronomical objects because they extensively differ from the distances that can be calculated quite easily by employing simple technique of geometry. The discrepancy starts right from Andromeda Galaxy thus any excuse of the ‘curved spacetime’ over very long distance will not work. Actual and strict finding of Edwin Hubble was only that there is linear relationship between ‘redshift’ and ‘distance’ and to be precise, for Hubble, the reason of redshifts is not known[xiii]. But unfortunately, official science has adopted ‘velocity’ as a valid reason of redshifts. With redshifts being interpreted in terms of ‘velocity’, the formula of those redshifts contains ‘c’ i.e. the value of speed of light. With ‘c’ included in the formula, ‘v’ (velocity) will never reach closer to ‘c’ or the results will be twisted may be in some other way.
Now within next few years[xiv], NASA is going to launch James Webb Space Telescope which is said to be 100x more powerful[xv] than highly successful predecessor Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The strange aspect is that despite 100x power of upcoming new space telescope, NASA is dead sure that no galaxy beyond 13.6 billion light years will be seen[xvi]. NASA explains that Big Bang occurred 13.8 billion years before – although the upcoming telescope will not be able to see Big Bang itself but the very first galaxies belonging to the distance of 13.6 billion light years will be resolved whereas nothing will be seen beyond that distance because actually there was no light at all before that era.
The fact is only that due to twisted formulas, actually the ‘distance’ will never be shown greater than certain value. The reason behind the absolute surety of NASA that any galaxy older than 13.6 billion years will not be seen by the 100x more powerful telescope is the fact that NASA is fully aware[xvii] that limit on distance is imposed by the formula itself. Please see the following table of different values of redshifts (Z) and corresponding distances of galaxies in light years:

Redshift-distance relationship that should be expected to be tabulated here in simple linear format where certain increment in redshift should result in regular (linear) increment of distance, actually has been implemented in a twisted form such that with increase of value of ‘z’ (redshift) after the value 2, there is decreasing trend of distance which means that distance is not being increased properly in official tables. For example with increment of 1 in the value of z from 1 to 2, the corresponding increment in the distance is almost 3 billion light years. But afterwards with the increments in z from 4 to 5 to 6 to 7; not a single billion light year is incremented on the distance scale. Clearly this is the consequence of including value of ‘c’ in the formula of redshift. At redshift 10, galaxies are ‘moving away’ at speed close to ‘c’. When receding speed (if really receding) of galaxy will further approach towards ‘c’, the galaxy will no more be visible. While the formula intends to restrict visibility within the range of below luminal receding speeds but another factor is on the play. The sort of cosmic horizon beyond which HST cannot see is not actually determined by receding speeds of galaxies because galaxies are not in fact receding away like that. Actually there is region beyond (official) 13.2 billion light years where galaxies are considerably redshifted to near infrared zone that HST cannot see. James Webb Space Telescope is able to see infrared portion objects but that also has limit. With these hard compulsions that come mainly from calculation methodology, NASA conveniently asserts that beyond 13.6 billion light years, there will be complete darkness and the darkness will be due to absolute absence of galaxies. Galaxies did not exist prior to 13.6 billion light years and the Big Bang Theory is directly confirmed through a powerful telescope, even before the launch of the telescope. With too expensive project of prestigious space telescope that is not even going to have long functional age, the maximum they are going to find or deliberately want to show is that galaxies do not exist beyond the distance of 13.6 billion light years; age of universe i.e. 13.8 billion years is correct; Big Bang Theory is therefore ‘confirmed’ at ‘observational level’. Furthermore, we have already seen in first chapter that these formulas serve as colored spectacles and result is that if real or even hypothetical galaxy is located beyond 14 billion light years, the formula will tell that it is not located at distance more than 13.6 billion light years. So here need is to look at the reality with clear objective eyes and vision which is not contaminated by the colored spectacles.
MS. Tamara M. Davis is an official voice who tells these things slightly differently. In a paper titled “Superluminal Recession Velocities”[xviii] she and co-author write that official redshift formulas are taken within the context of Special Theory of Relativity (SR) that requires that visibility of galaxies should stop when ‘v’ becomes equal to ‘c’ i.e. when receding velocity equals velocity of light, then the galaxy permanently goes out of sight.
Thus, galaxies with distances greater than D = c/H are receding from us with velocities greater than the speed of light and superluminal recession is a fundamental part of the general relativistic description of the expanding universe. This apparent contradiction of special relativity (SR) is often mistakenly remedied by converting redshift to velocity using SR.
Being Physicists who prefer General Relativity (GR) over SR and who are straightforward in their assertions, the authors of this paper reveal the secret that galaxies having value of redshift more than 3 are actually receding away at superluminal speeds.
Here we show that galaxies with recession velocities faster than the speed of light are observable and that in all viable cosmological models, galaxies above a redshift of three are receding superluminally.
Afterwards this paper proceeds to explain the mechanism by which galaxies ‘recede away at superluminal velocities’ but still remain visible in terms of ‘curved spacetime’ model of GR.
Now we come back to our book where the point is not SR or GR. Cosmic Redshifts do not in fact mean ‘velocity’; galaxies are not moving away at all. The actual fact is that galaxies having redshift more than 3 are located beyond the official time of Big Bang. Confidence of NASA that even 100x powerful telescope will not be able to see anything beyond the distance of 13.6 billion light years indicates that NASA is fully aware that limit is imposed by the formula itself. That is, even if they find lot of galaxies located at very far off actual distances, they will conveniently say the distance is not more than 13.6 billion light years by showing the ‘calculated’ distance as proof.
Mr. Marco Pereira[xix], MSc (Nuclear Physics), PhD (Physical Chemistry) and a Professor of Molecular Bio-Physics has also noted the anomaly of non-linear ‘observations’ of redshift-distance in Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) data[xx]. He claims to have found fourth spatial dimension in the Universe through his self-created theory of ‘Hypergeometrical Universe’[xxi]. He claims that his theory has rightly predicted non-linear redshift-distance pattern of Super Novas 1a which is actually observed by SDSS.

Above type of non-linear observed redshift-distance relationship is claimed to be rightly predicted by his theory of Hypergeometric Universe and the same is said to be the proof for the existence of extra spatial dimension of the Universe. We have noted already that actual non-linear redshift-distance relationship is something which mainstream physicists avoid to mention and only few people like MS. Tamara M. Davis would dare to expose this kind of secret. Our finding is that Mr. Marco Pereira has not found some reality which was already not calculated by Special Relativity but he does reach to a position which is normally not told openly by the mainstream physicists. After sensing this anomaly, MS. Tamara M. Davis rejected SR based calculations and favored GR based explanation. After finding that same anomalous looking SDSS observations are consistent with his Theory of Hypergeometric Universe which accommodates SR formulas in its development, Mr. Marco Pereira declares that SDSS observations are the proof of the existence of extra fourth dimension of the Universe. Underlying fact is that SDSS has also calculated distances of 1a Super Novas using the formulas of Special Relativity. The Lorentz Transformation factor is the reason behind non-linear plotting of this data. According to simple Hubble Law, the plotting should have been linear. If it is actually linear which becomes possible if we remove Lorentz Factor from the formulas of redshifts then distances of farthest visible galaxies come at the scale of many hundreds of billions light years which are consistent with direct simple geometric calculations of distances. The ground for removing Lorentz Factor from formulas of redshifts is the fact that redshifts do not actually represent velocities. But if redshifts do represent velocities (i.e. the position which is official but not likely) then non-linear plotting of real redshift-distances data is actually an anomaly that can rightfully be accounted for by proposing a fourth dimension of the Universe. In case Universe is actually expanding and farther galaxies are more redshifted at those distances which are lesser than the expected linear distance then extra redshift might have been accumulated during the course of passage of those galaxies through the “fourth dimension” proposed by Mr. Marco Pereira. The result is that either farthest visible galaxies are located at the distance scale of many hundred billion light years or Mr. Marco Pereira may be right in his proposal of extra fourth dimension of the Universe.
But reality is not that complex as suggested by Mr. Marco Pereira who only apparently favors simplicity by attributing his complex theories as conforming of Occam’s razor[xxii]. The proof of the assuredly far greater distances of astronomical objects as presented in this section is as straightforward as it can get and thus conforms to the Occam’s razor in true sense. Readers are requested to recalculate these distances by themselves and also recheck the results with official Trigonometric Formulas whose results, with lower side estimates of diameters involved, are only slightly different as given in table below.

It is stated already that Expansionist regime is not entirely blank about these anomalies. They know these things and they hide the actual things by presenting them within twisted terminology and formulas of their favored framework. The Wikipedia article titled “Angular diameter distance”[xxiii]contains following important, though twisted, confession about this topic:
However, in the ΛCDM model (the currently favored cosmology), the relation is more complicated. In this model, objects at redshifts greater than about 1.5 appear larger on the sky with increasing redshift.
This is related to the angular diameter distance, which is the distance an object is calculated to be at from ɵ and x, assuming the Universe is Euclidean.
We have seen already that in official tables, with the increase of redshift, the increment in the distance scale becomes shorter and shorter. Formula tells that astronomical object is located at nearer than the actual distance and thus the object ‘appears’ (within standard model) larger on ‘sky’. Appearance on sky of anything does not depend on any model. If something is looking larger on sky within Lambda CDM model, then it only means that calculated size of object is larger than what can be actually observed on sky. We also have seen earlier in this section that just how Andromeda ‘appears’ larger on sky. This confession, though made in twisted words, automatically validates, in principle, the calculations about tremendously larger distances of visible galaxies presented in this section. Therefore the only issue remained unsettled so-far is to check whether Universe is really Euclidean or not. The dilemma of the official cosmology is that now they have reached to the finding that at least observed universe is flat and thus the actual geometry of the observable universe is Euclidean. In a flat universe which is representable using Euclidean geometry, the two parallel lines will always remain parallel no matter how great distance is covered. To a question “Is the universe really flat, or is it just very slightly curved?” – Mr. Erik Anson, Physics/Cosmology PhD student (University of Washington) provided following insightful reply[xxiv]:
Yes, it’s entirely possible that the Universe is only almost flat on large scales, as is acknowledged by the (scientific)[xxv] community. There is a cosmological parameter, Ωk, that relates to the amount of large-scale curvature, and observations can constrain it to be within a small range including zero, but can never show it to be exactly zero.
However, if there is any curvature, it’s so small that it’s effectively irrelevant, so we may as well model it as flat (which is simpler) unless and until we know otherwise.
Symmetry magazine[xxvi], which is a joint publication of ‘Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory’ and ‘SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory’ published an article titled “Our Flat Universe – Not a curve in sight, as far as eye can see”[xxvii] on date 07-04-2015. The following introductory lines say it all that observable universe is actually found out to be flat and thus representable in Euclidean geometry:
Mathematicians, scientists, philosophers and curious minds alike have guessed at the shape of our universe. There are three main options to choose from, in case you’d like to do some digging of your own:
The universe could be positively curved, like a sphere.
The universe could be negatively curved, like a saddle.
The universe could be flat, like a sheet of paper.
As far as scientists can tell, this third option is correct. But what do people really mean when they talk about “flatness”? Your high school math teacher would be overjoyed to tell you that it’s all about geometry.
In a flat universe, Euclidean geometry applies at the very largest scales. This means parallel lines will never meet, and the internal angles of a triangle always add up to exactly 180 degrees—just like you’re used to.
In Lambda CDM model, as we have seen, the distances of far off galaxies are not the actual physical distances as they are superimposed and artificially constrained by the twisted formulas. In simple geometric calculations of distances, there is no artificial or twisted superimposition at work and thus actual distances of visible galaxies really are on a much larger distance scale than could be permitted by the standard model which means that the actual physical reality is not truly ‘modelled’ by this ‘standard model’. With extremely greater distances of astronomical objects, the problem is not that there should be more than observable matter; the implication is that density of matter within the universe is far lower than the available assessments of the so-called standard model who has false claim of having explained all the observed reality because the model does not even know the right density of present day Universe and still claims to know all the details of minute fractional parts of so-assumed very first moment after the ‘Big Bang’. Secondly, it is due to ‘velocity’ interpretation of redshifts that whole need of using ‘c’ in the redshift formulas arise. It is value of velocity of light ‘c’ which compels science authorities to stay blind with wrong lower side estimates of distances of remote galaxies. Velocity interpretation of redshifts inescapably leads towards flawed calculations of the distances of those galaxies which is sort of mathematical proof that redshifts do not represent receding velocities of galaxies because with velocity interpretation, ‘c’ will be added in the formulas of redshifts; consequently the estimates of astronomical distances would be bound to be outright deceitful as no galaxy will be shown located beyond a certain distance. And although better estimates of astronomical distances have been presented in this section but this book will keep on referring to the distances of remote galaxies with ‘standard’ values or estimates unless otherwise specified.
[i] https://lco.global/spacebook/using-angles-describe-positions-and-apparent-sizes-objects/ , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angular_diameter and diameters of Sun and Moon taken from simple google search.
[ii] Britannica article on Coma Cluster says that diameter is 25 million light years. [The main body of the Coma cluster has a diameter of about 25 million light-years]. Wikipedia article seems silent on diameter but google search show up from reference of Wikipedia that diameter of Coma Cluster is 20 million light years.
[iii] “Angular Diameter Distance” section on this Wikipedia page: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Distance_measures_(cosmology)
[iv] “Distance Estimates” section of Andromeda article on Wikipedia — https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andromeda_Galaxy
[v] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andromeda_Galaxy
[vi] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andromeda_Galaxy
[vii] http://sci.esa.int/planck/47695-the-coma-cluster/
[viii] Based on comparison of section of sky of deep field image with size of moon on this and many other pages: http://mikkolaine.blogspot.com/2014/01/size-of-deep-sky-objects-compared-to.html
[ix] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andromeda_Galaxy
[x] https://jwst.nasa.gov/galaxies.html
[xi] https://earthsky.org/astronomy-essentials/galaxy-universe-location
[xii] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GN-z11
[xiii] https://khuram-on.quora.com/Meaning-of-redshifts-according-to-Edwin-Hubble
[xiv] Right now, the space telescope is expected to be launched in year 1921. https://jwst.nasa.gov/about.html
[xv] https://www.techtimes.com/articles/2714/20140115/forget-hubble-100x-more-powerful-james-webb-telescope-is-getting-prepped.htm
[xvi] https://jwst.nasa.gov/firstlight.html
[xvii] I had little conversation (over Internet) with a NASA Information Officer. I told him that official galactic distances are underestimated. I did not explain or prove my point; just told that proof will come with book (i.e. this book). He denied the existence of any such anomaly and also denied that NASA is trying to hide this anomaly. To this I replied that even then I will write in my book that NASA fully knows and only hides this fact because otherwise it will be more embarrassing for NASA. Readers should judge by themselves whether or not NASA knows about it given the simple fact that their formulas do impose upper limit on distance of galaxy.
[xviii] https://arxiv.org/pdf/astro-ph/0011070v2.pdf
[xix] Quora.com profile of Mr. Marco Pereira – https://www.quora.com/profile/Marco-Pereira-1
[xxi] http://www.worldscientificnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/WSN-98-2018-127-139.pdf
[xxii] https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Occam%27s_razor
[xxiii] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angular_diameter_distance
[xxiv] https://www.quora.com/Is-the-universe-really-flat-or-is-it-just-very-slightly-curved/answer/Erik-Anson
[xxv] Bracket (scientific) added by me.
[xxvi] https://www.symmetrymagazine.org/about
[xxvii] https://www.symmetrymagazine.org/article/april-2015/our-flat-universe